Test tube treatment
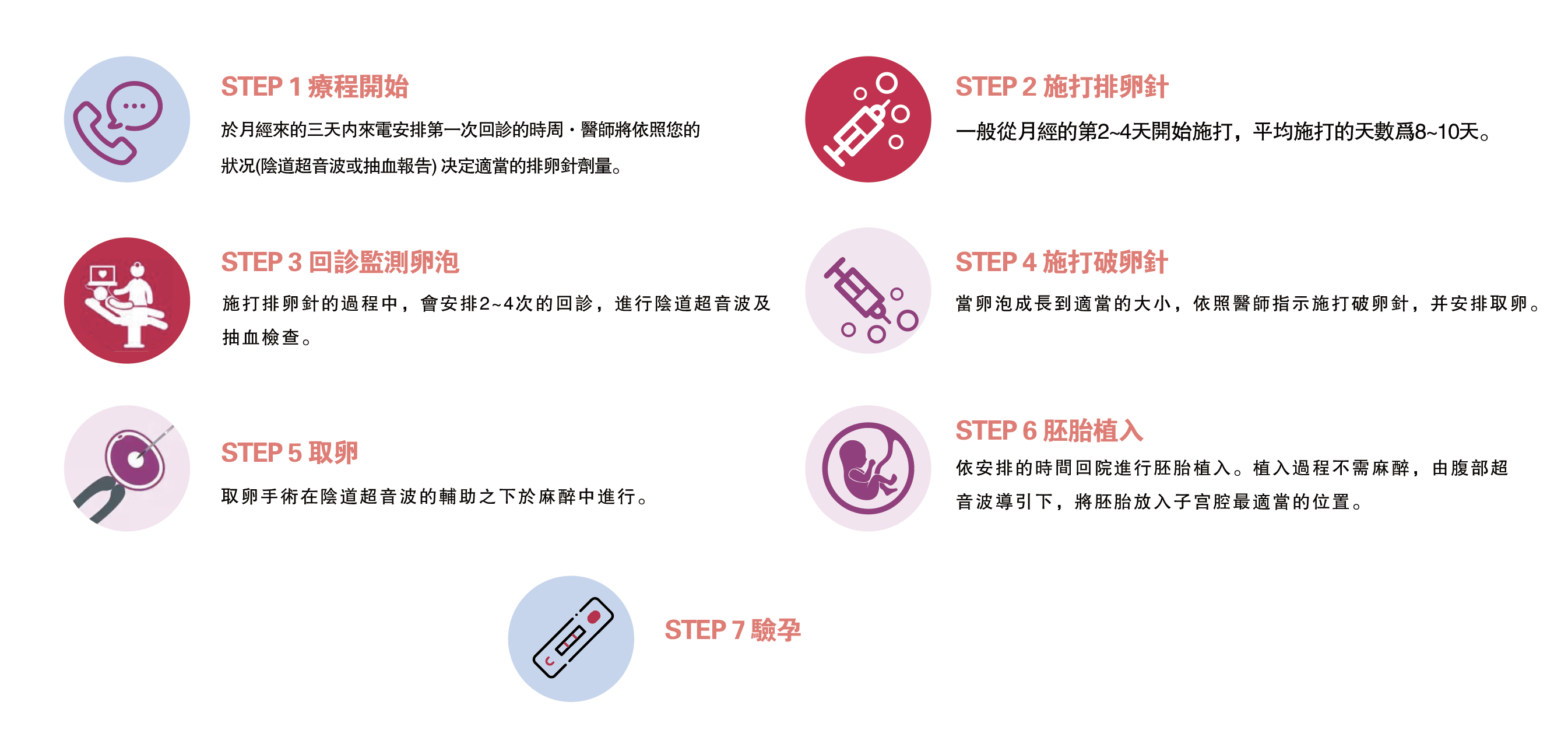
Ivf procedure
The first generation of test tubes
Test-tube babies are academically called in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer (IVF-EF), that is, the eggs are removed by surgery and the processed sperm are fertilized outside the body. After the fertilized egg develops outside the body for three to five days, it is moved to the uterus for implantation and development. According to statistics, the average pregnancy success rate of a cycle of IVF is about 50%, but it varies according to age and the cause of infertility. For women over 40 years old, the success rate drops to 25%, and even drops to 10% for women over 43 years old.

Second-generation test tube
Under normal circumstances, when the sperm and the egg meet, the sperm will penetrate the transparent layer outside the egg and then combine with the egg and fertilize it. However, under certain circumstances, when the sperm cannot naturally fertilize the egg, you need to use Artificially, under a microscope, a single sperm is taken, and a single sperm is injected into the egg with a special needle to fertilize it. This fertilization method is called intracellular sperm microinjection.

Three-generation test tube
The third-generation test-tube baby technology is also called preimplantation genetic diagnosis/screening , which refers to the analysis of the genetic material of the embryo before the IVF-ET embryo transfer , diagnosis of abnormalities, and screening of healthy embryo transfer , a method of preventing the transmission of genetic diseases . The test substance is taken from one cell of an embryo at the stage of 4 to 8 cells or the first diode of an egg before and after fertilization . Sampling does not affect embryonic development. Single-cell DNA analysis is used for detection , one is polymerase chain reaction ( PCR ), which detects gender and single gene genetic diseases ; the other is fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), which detects gender and chromosomal diseases . The third-generation test-tube baby technology can carry out sex selection , but only when the offspring’s sex chromosomes are likely to be abnormal and bring serious consequences, sex selection is allowed. Essentially, third-generation IVF technology selects disease, not sex.


